Disclaimer: I am a consultant at Amazon Web Services, and this is my personal blog. The opinions expressed here are solely mine and do not reflect the views of Amazon Web Services (AWS). Any statements made should not be considered official endorsements or statements by AWS.
In this post, I'll show how to use Serilog in a .NET Worker Service to perform Structured Logging and persist log data to AWS CloudWatch.
You will also learn how to use AWS CloudWatch Log Insights to query log data to determine how structured logging can benefit you.
Open Visual Studio, create New Project, and select Worker Service template.
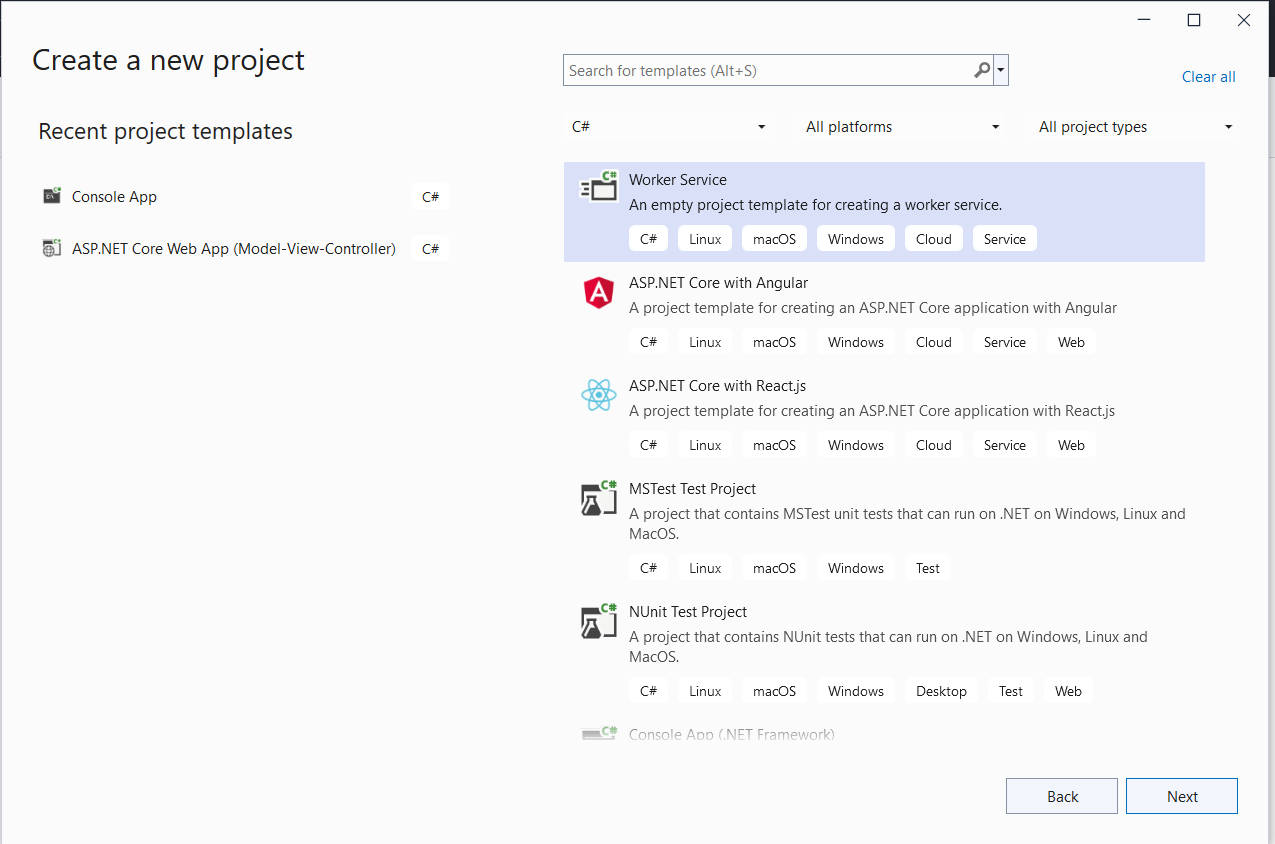
On the next dialog, enter Project Name and select Next. Select the latest framework, I am selecting .NET6 for now.
To add Serilog to your .NET Worker Service (Non-Web) application, install the following NuGet packages.
Serilog.Extensions.Hosting - This package provides an extension method UseSerilog() to add Serilog provider to Non-web .NET Core applications. Since this package depends on Serilog, it automatically installs that as well.
Serilog.Settings.Configuration - This package allows you to read Serilog configurations from Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration sources, including .NET Core's appsettings.json file.
Serilog provides sinks for writing logs at various destinations. Here is a complete list of supported sinks. To follow this blog post, you can just install the following sinks.
Serilog.Sinks.Console - This package writes logs to Console.AWS.Logger.SeriLog - This package writes logs to AWS CloudWatch. This is an official NuGet package managed by AWS.Open Program.cs file, and update the code as shown below.
The preceding code uses UseSerilog() extension method to add the Serilog logging provider to your application. Next, it reads configuration from IConfiguration sources, which is appsettings.json for this demo. Finally, it adds support for structured logging from the Enrich.FromLogContext() line.
Now let's modify appsettings.json file to add Serilog configuration.
Finally, edit worker.cs file and update the code to include a logging statement as shown in the following code snippet.
Build and run the application by pressing F5, you should see the logs in Console as shown shown below.
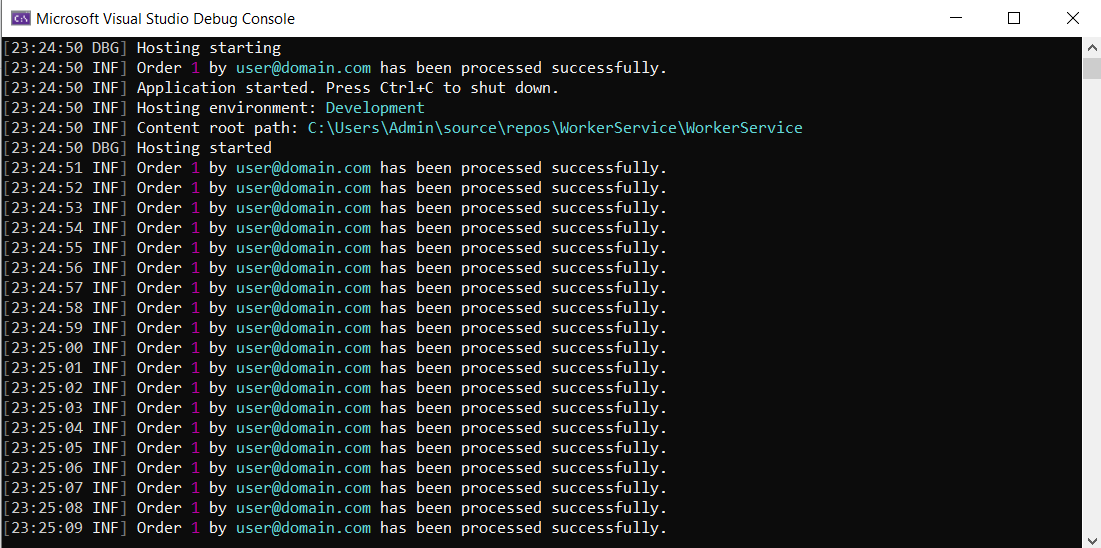
Logs generated in the previous step have also been written to AWS CloudWatch automatically through the configured CloudWatch sink.
Follow the instructions below to view the logs in AWS CloudWatch.
Go to AWS CloudWatch and see the output for structured logging. As you can see, the logs are in JSON format rather than plain text.
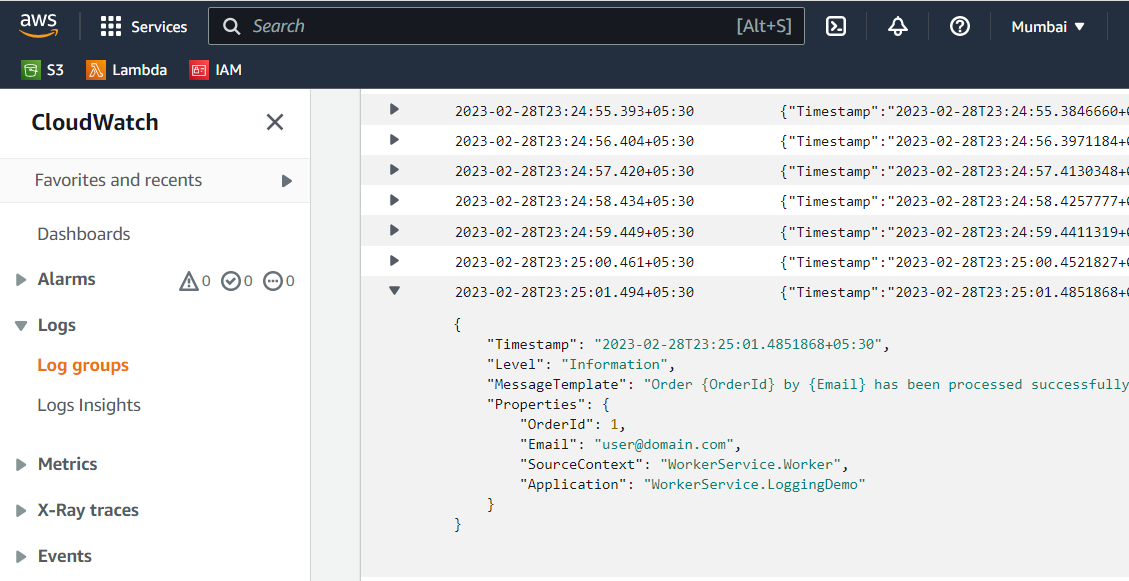
Next, go to AWS CloudWatch, and select Logs Insights.
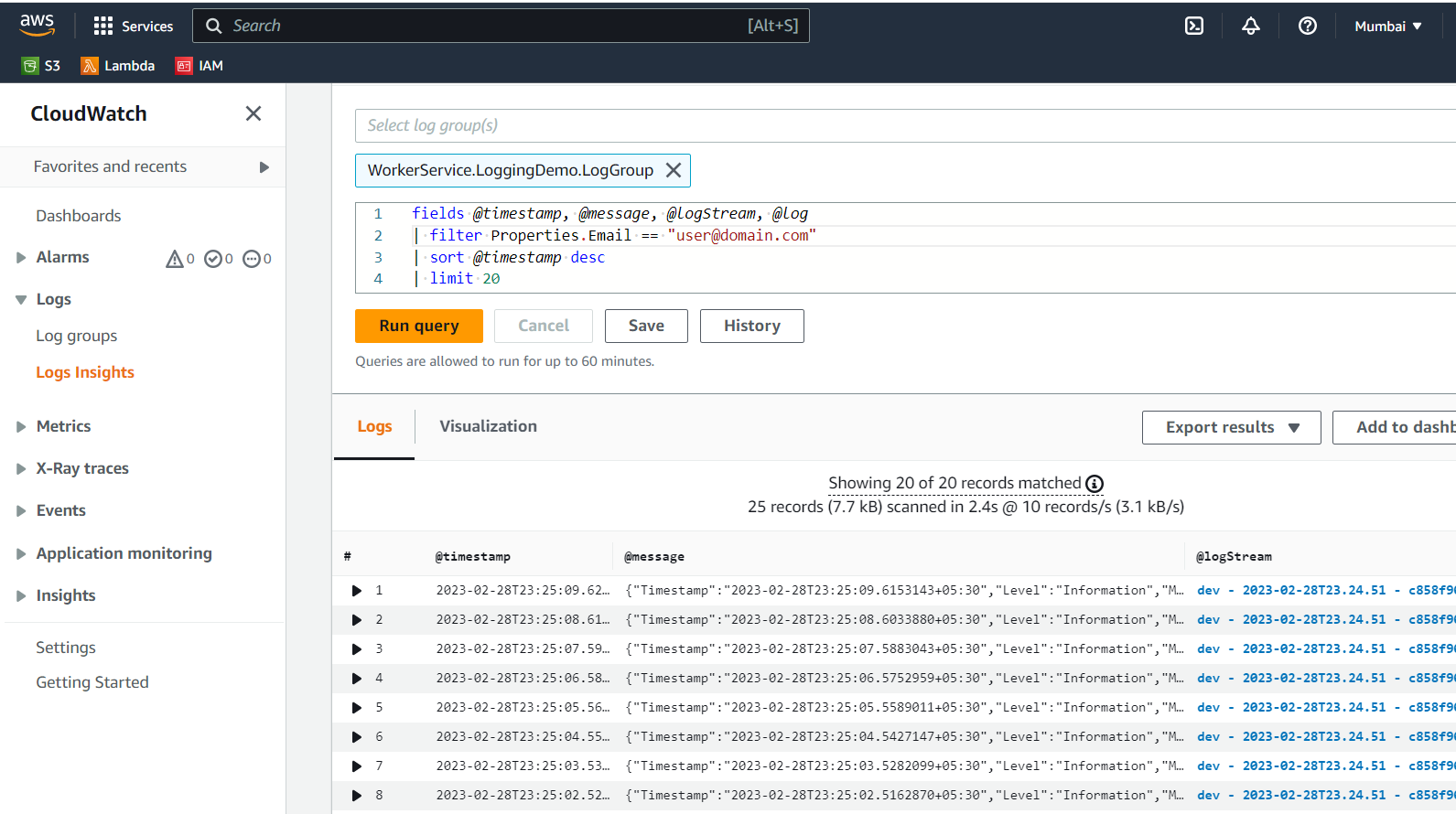
Select the Log Groups from the dropdown and write a query to filter logs.
See the below screenshot of the filtered logs in AWS CloudWatch Logs Insights.
In this post, you learned how to use Serilog to perform structure logging in AWS CloudWatch from your .NET Worker Service. Please share your views and feedback in the section below.
Thank You ❤️

