Disclaimer: I am a consultant at Amazon Web Services, and this is my personal blog. The opinions expressed here are solely mine and do not reflect the views of Amazon Web Services (AWS). Any statements made should not be considered official endorsements or statements by AWS.
In this post, we will understand how to use Serilog in AWS Lambda to store logs in AWS CloudWatch.
We will be using the below tools and frameworks in this post going forward.
Open Visual Studio, and create a new project with AWS Lambda Project template as shown in the below picture. To get AWS project templates, you have to install AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio first.
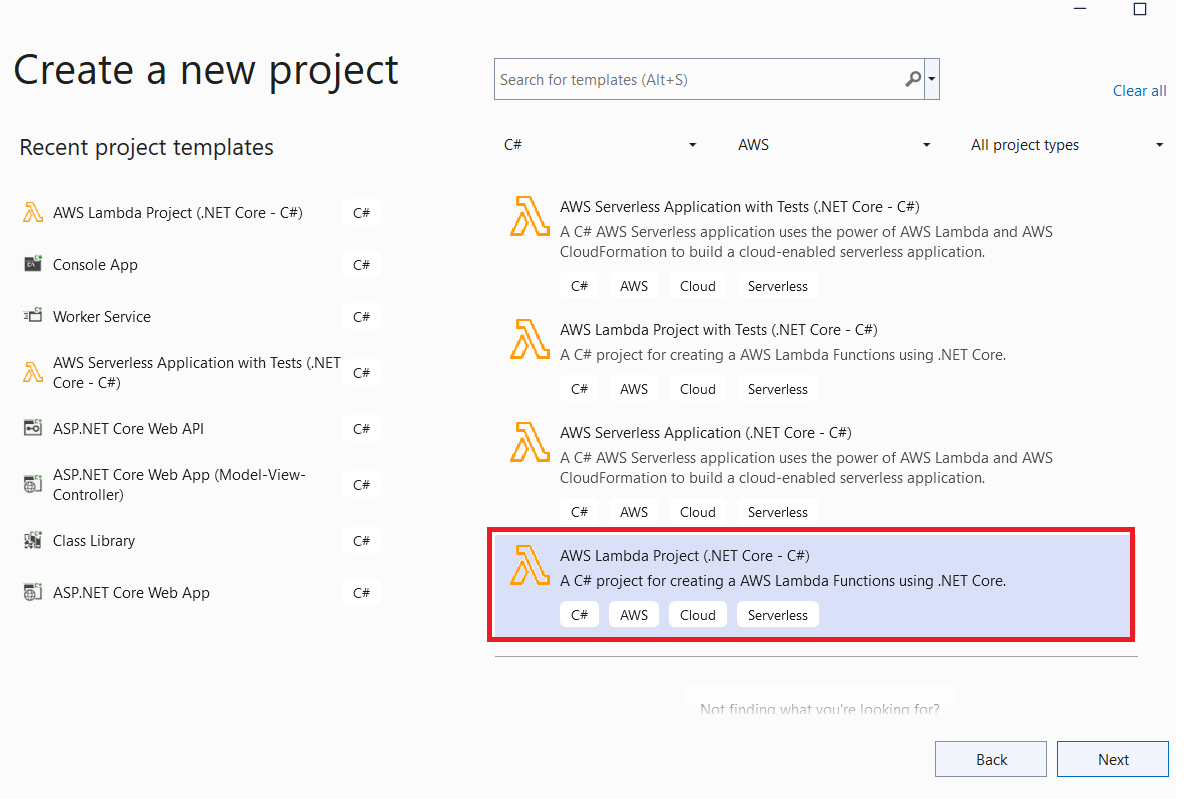
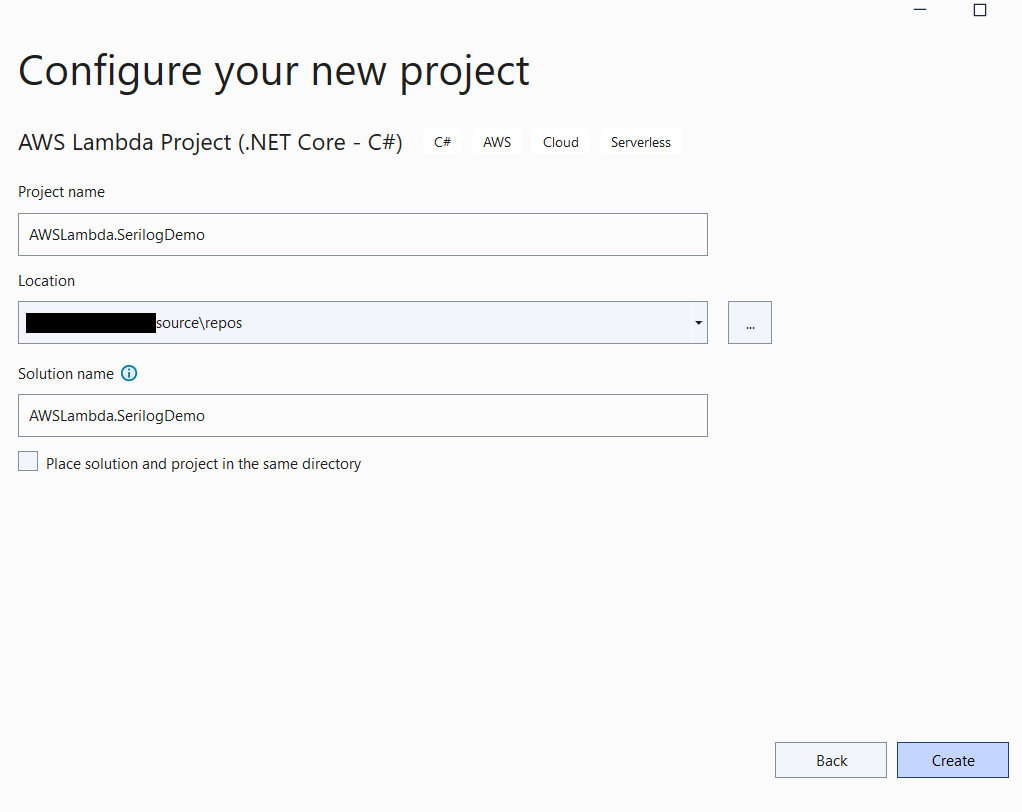
In the next step, provide some necessary information as per the below picture, and then click on create button.
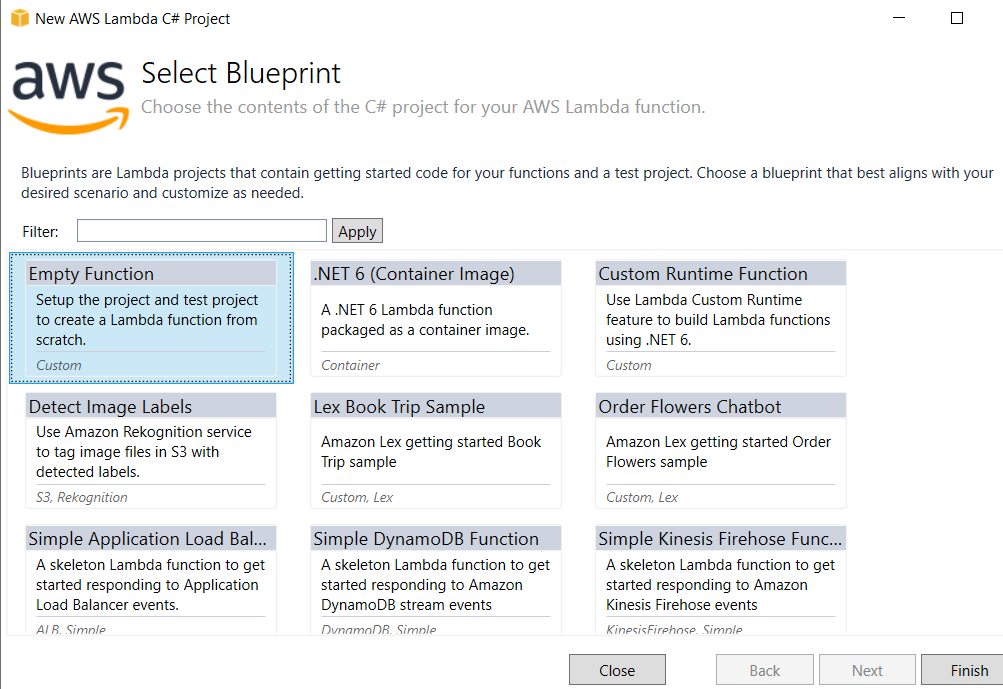
Now, select a Blue Print as per your application's need. Here, I am selecting Empty Function to keep things simple.
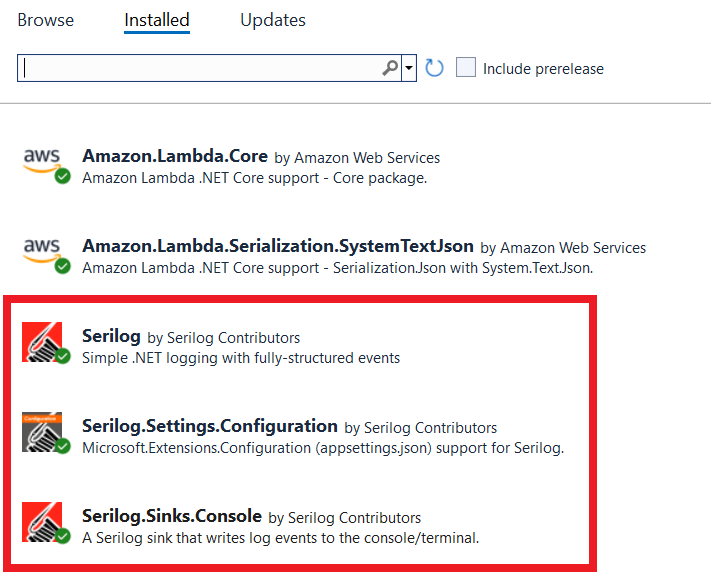
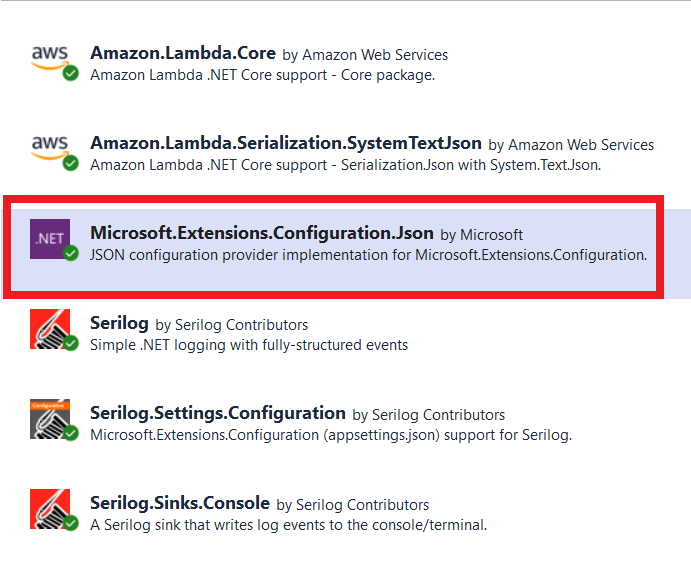
Install the following NuGet packages to install Serilog in your Lambda Function.
appsettings.json.In this picture, you can see we have installed above mentioned NuGet packages.
Important: By default, everything that we write to the Console from within an AWS Lambda function, ends up in AWS CloudWatch, so if we are writing to the Console via
Serilog.Sinks.Console, then all the logs by default will get stored in the AWS CloudWatch log group. We don't have to do anything extra for this.
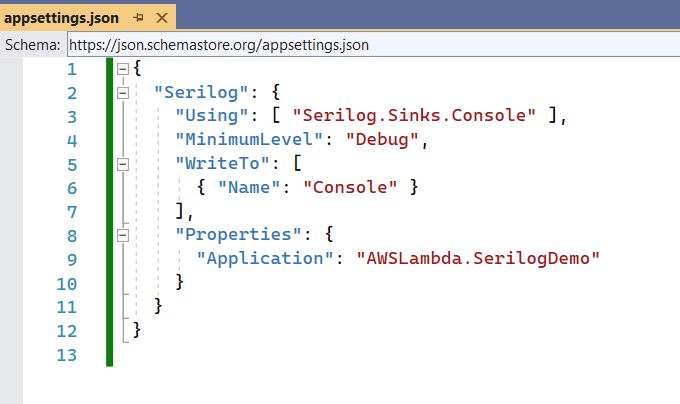
Create an appsettings.json file and copy the below configuration there. You can modify this configuration as per your need, but for this demo, this configuration is sufficient.
Also, don't forget to set Copy to Output Directory property to Copy always for appsettings.json file.
Your appsettings.json file should look like the below:
Install Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json NuGet package to read configurations from appsettings.json file.
After installing the above NuGet package, you can initialize the Serilog logger by reading the configurations from appsettings.json file inside the constructor.
Once Serilog is initialized, you can use the below logging methods.

You can copy the above code from here.
Right-click on the Lambda project and select Publish to AWS Lambda... This will open up below the window. Verify all the information and click on Next.
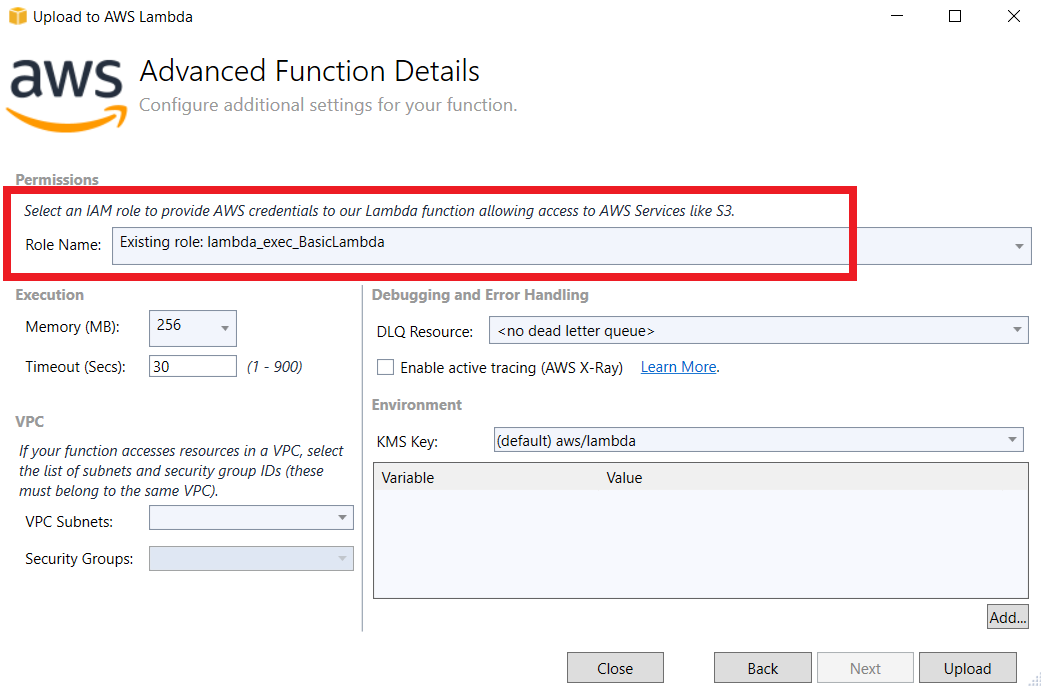
In this window, make sure you select the lambda_exec_BasicLambda role. This basic lambda role has enough permissions required to store the logs into AWS CloudWatch.
Once Lambda Function is deployed successfully, we can test it by invoking it from the Visual Studio itself. You can see the below picture, log information is getting printed, which means Serilog is doing its job.
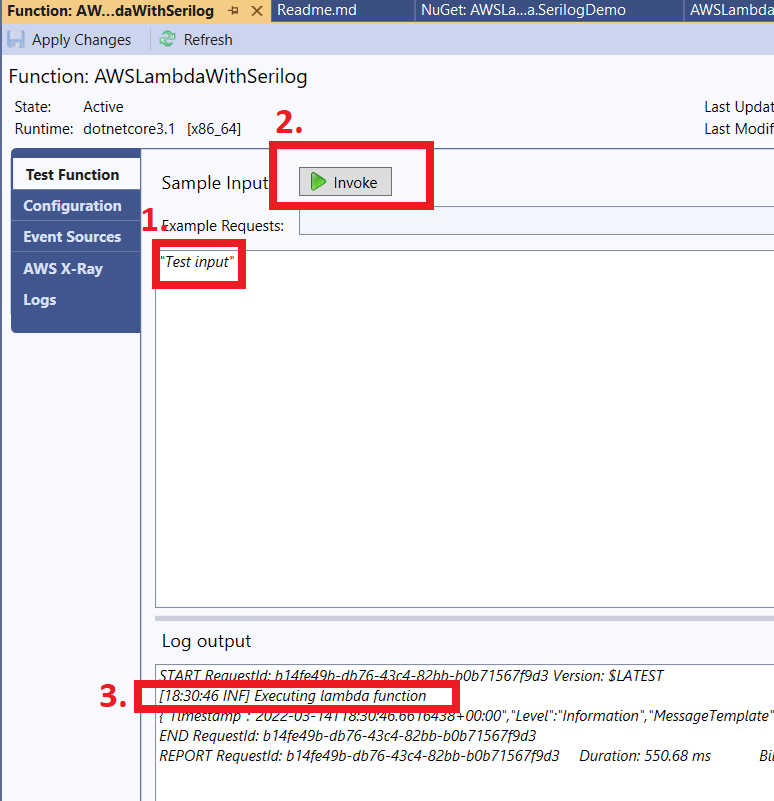
We can also verify it from the AWS CloudWatch console.
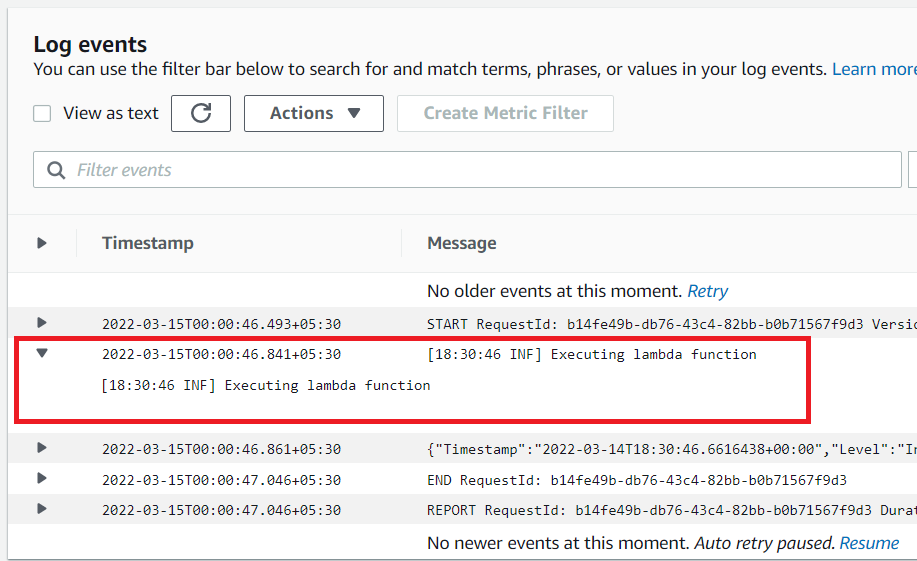
That's all.
In this post, we learned how easily we can start using Serilog in AWS Lambda in less than 10 minutes. Please let me know your thoughts and feedback in the comment section below.
Thank You ❤️

